PSORIASIS - PART 1
- Dr. Moran Sciamama Saghiv

- Oct 15, 2025
- 6 min read
Disclaimer: The content of this blog post, authored by Dr. Moran Sciamama-Saghiv, is provided for informational and educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. No doctor–patient relationship is created by reading or applying the information. Readers should always consult a licensed healthcare professional before making decisions related to medications or treatment. Neither the author nor any affiliated party assumes any liability for actions taken based on this content.
My aunt Lillian (R.I.P.; dad's sister) had sever Psoriasis in her feet. I remember that when I was about 25 years old, my dad asked me if I could make the time to take her to the Dead Sea. Once a month, I would pick her up from her home, and spend half a day with her driving her from home and back, and waiting for her to finish bathing in the Dead Sea. I remember the relief it brought her...
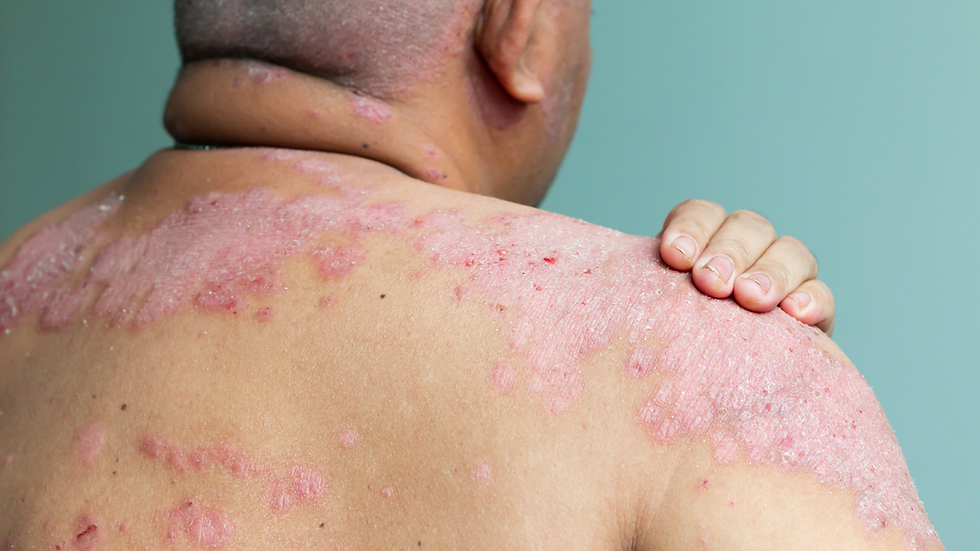
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects millions globally, with recent estimates indicating around 125 million people affected. This condition manifests as red, scaly patches on the skin, causing discomfort and self-consciousness. Understanding psoriasis is vital not only for those diagnosed but also for their families and friends. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available for psoriasis, giving you a thorough overview of this condition.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is more than a skin issue; it's a complex disease involving the immune system. The body mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to rapid skin cell production. This accelerated growth creates the characteristic plaques many associate with psoriasis. While the exact cause remains unclear, research suggests that a combination of genetic, environmental, and immune system factors plays a role. For instance, those with a family history of psoriasis may have a 10-20% higher risk of developing the condition.
Types of Psoriasis
There are several types of psoriasis, each with unique attributes. The most common types include:
1. Plaque Psoriasis
Plaque psoriasis is the most prevalent form, affecting 80-90% of those diagnosed. It appears as raised, red patches covered with thick, silvery scales, commonly on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. In fact, around 50% of individuals with plaque psoriasis experience moderate to severe symptoms that significantly impact their daily lives.
2. Guttate Psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis usually begins in childhood or young adulthood. It is characterized by small, drop-shaped lesions that typically show up on the trunk, arms, and legs. Interestingly, this type can often be triggered by infections like strep throat, occurring in about 5-10% of all psoriasis cases.
3. Inverse Psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis presents as smooth, red patches in skin folds such as under the breasts, in the groin, or around the buttocks. This type tends to be less scaly and can worsen due to friction and sweating, making it particularly uncomfortable.
4. Pustular Psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis features white pustules (noninfectious blisters) surrounded by red skin. It can occur in localized areas or cover large parts of the body and may be severe enough to require immediate medical attention in about 20% of cases.
5. Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Erythrodermic psoriasis is a rare but serious form that can cover the entire body with a red, peeling rash that itches or burns intensely. This type necessitates urgent medical care, as complications can arise if left untreated.
Symptoms of Psoriasis
The symptoms of psoriasis can differ widely among individuals. Common symptoms include:
Red patches on the skin covered with thick, silvery scales
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
Itching, burning, or soreness
Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails
Swollen and stiff joints, particularly in cases of psoriatic arthritis
Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to more effective management of the condition.
Triggers of Psoriasis
Identifying triggers can help you manage flare-ups more effectively. Common triggers include:
Stress: High stress levels can worsen symptoms; studies show that over 60% of individuals report stress as a significant trigger.
Infections: Certain infections, especially strep throat, have been known to trigger guttate psoriasis in approximately 30% of cases.
Skin Injury: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburns can lead to new patches.
Weather: Cold, dry conditions often worsen symptoms, while about 30% of people find sunlight beneficial.
Medications: Some medications, including lithium and beta-blockers, can exacerbate psoriasis or trigger new cases.
By tracking and understanding your triggers, you can take proactive steps to manage your condition.
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
If you suspect psoriasis, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. A dermatologist will usually carry out a physical examination of your skin, nails, and scalp. Occasionally, a skin biopsy may be necessary to eliminate other skin conditions.
Treatment Options for Psoriasis
While there is no cure for psoriasis, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and enhance your quality of life. Treatment plans are typically customized based on the severity of the condition.
1. Topical Treatments
Topical treatments often serve as the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis. These include:
Corticosteroids: These reduce redness and itching and are effective in over 70% of mild psoriasis cases.
Vitamin D analogs: These slow skin cell growth, making them effective against plaques.
Retinoids: Vitamin A derivatives that can normalize skin cell production.
Calcineurin inhibitors: These reduce inflammation and plaque formation for sensitive areas.
2. Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet light under medical supervision. This treatment can be effective for those with moderate to severe psoriasis when topical treatments prove insufficient.
3. Systemic Treatments
For severe psoriasis cases, systemic treatments might be required. These medications work throughout the body and include:
Oral medications: Methotrexate, cyclosporine, and acitretin are common.
Biologics: Targeting specific parts of the immune system, biologics are typically prescribed for moderate to severe psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis and have shown improvement rates of 75% or more in many patients.
Lifestyle Changes and Home Remedies
Alongside medical treatments, certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can aid in managing psoriasis symptoms. Here are some practical tips:
Moisturize regularly: Keeping your skin hydrated can reduce dryness and scaling.
Lukewarm baths: Adding oatmeal or Epsom salts can soothe irritated skin.
Avoid triggers: Identifying and steering clear of personal triggers can minimize flare-ups.
Balanced diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats can support overall health.
Stress management: Techniques like yoga, meditation, or simple deep-breathing exercises can help keep stress levels down.
Final Thoughts
Psoriasis is a complex condition that requires a multi-faceted approach to management. By grasping the types, symptoms, triggers, and available treatment options, you can take control of your health and improve your quality of life. In the next part of this series, we will explore the emotional and psychological impact of psoriasis, as well as support resources available for those affected. Stay tuned for more insights and practical advice on living with psoriasis. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; there are many resources and communities available to support you.
Services by Dr. Moran Sciamama Saghiv:
Tags associated with this blog post:
psoriasis, skin disease, autoimmune disorder, chronic skin condition, plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis, skin inflammation, itchy skin, red patches, scaly skin, dry skin, flaky skin, cracked skin, skin lesions, skin plaques, silvery scales, skin redness, chronic inflammation, immune system disorder, T cell overactivity, skin renewal, epidermal turnover, psoriasis flare, triggers of psoriasis, stress and psoriasis, genetics and psoriasis, family history, immune response, infection trigger, strep throat, smoking and psoriasis, alcohol and psoriasis, obesity and psoriasis, weather and psoriasis, cold weather, skin dryness, skin irritation, scalp psoriasis, nail psoriasis, joint pain, psoriatic arthritis, psoriasis symptoms, psoriasis causes, psoriasis treatment, topical creams, corticosteroids, salicylic acid, coal tar, vitamin D cream, phototherapy, UVB therapy, excimer laser, biologic therapy, biologics, immunosuppressants, methotrexate, cyclosporine, apremilast, inflammation control, immune modulation, dermatologist, skin specialist, psoriasis diagnosis, skin biopsy, skin care, moisturizing, emollients, skin hydration, gentle skin care, fragrance free products, skin barrier repair, stress reduction, mindfulness, yoga for psoriasis, diet and psoriasis, anti inflammatory diet, omega 3 fatty acids, vitamin D, antioxidants, healthy lifestyle, smoking cessation, alcohol moderation, mental health, depression and psoriasis, self esteem, body image, chronic illness management, patient support, psoriasis community, national psoriasis foundation, psoriasis awareness, autoimmune disease education, skin health awareness, holistic care, complementary medicine, natural remedies, home remedies, psoriasis triggers, flare up prevention, disease management, dermatology research, chronic condition care, inflammatory disorders, skin wellness, quality of life, chronic disease awareness, immune mediated disease.









Comments