SINGLE-LEG STANCE TEST
- Moran Sciamama-Saghiv
- Sep 4, 2025
- 4 min read
The Single-Leg Stance Test is a straightforward yet powerful tool for evaluating balance and stability. Whether you are an athlete looking to boost performance, a rehabilitation patient, or someone focused on improving fitness, this test is essential. In this guide, you will discover how to perform the Single-Leg Stance Test, its many benefits, and how to interpret your results effectively.
What is the Single-Leg Stance Test?
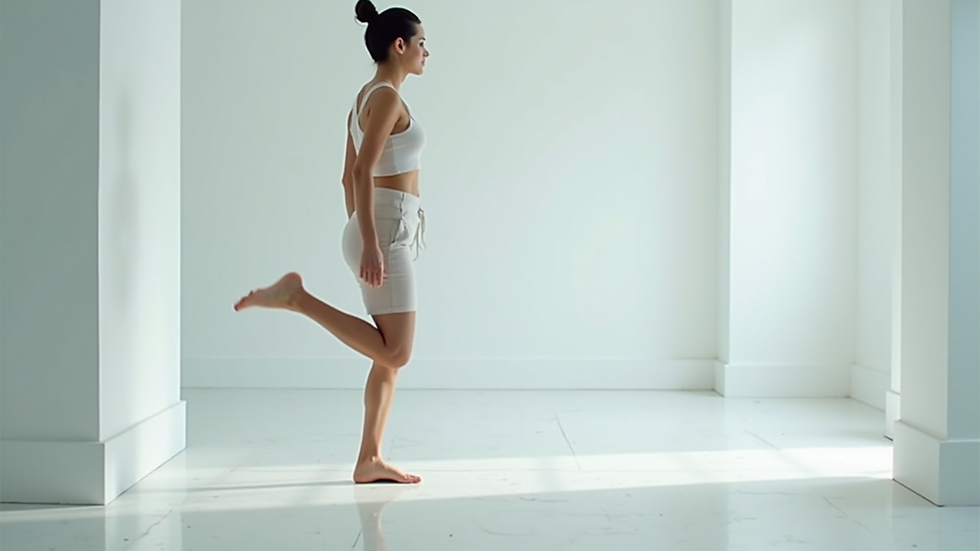
The Single-Leg Stance Test involves standing on one leg for a set time while keeping your balance. This test measures your ability to stabilize your body and control your center of gravity. It serves as a fundamental gauge of balance and can reveal important insights into your overall physical health.
Clinics often use this test for patients recovering from injuries, especially those concerning the legs and feet. However, it is equally useful for athletes and fitness enthusiasts aiming to track and enhance their balance over time. Studies show that maintaining balance is crucial for injury prevention, reducing the chance of falls by up to 50% in seniors.
How to Perform the Single-Leg Stance Test
Step 1: Prepare Your Environment
Ensure you have a safe space free of obstacles to prevent tripping. Find a flat surface where you can concentrate without distractions.
Step 2: Stand on One Leg
Choose a Leg: Select which leg to start with. Testing both legs helps to compare balance more effectively.
Position Yourself: Stand straight with your feet hip-width apart and shift your weight to the leg you chose.
Lift the Other Leg: Gradually lift the opposite leg off the ground by bending your knee at a 90-degree angle so that your foot hovers just above the floor.
Step 3: Time Your Balance
Start Timing: Utilize a stopwatch to measure how long you maintain your balance.
Maintain Your Position: Focus on keeping your body steady without leaning or using your arms for support.
Record Your Time: Stop the timer when you lose balance, indicated by touching the ground with your lifted foot or using your arms for stability.
Step 4: Repeat for the Other Leg
After checking your balance on one leg, switch to the other leg to repeat the test.
Step 5: Analyze Your Results
After timing both legs, compare your results. A significant difference may indicate an imbalance that could increase your risk of injury or impact athletic performance.

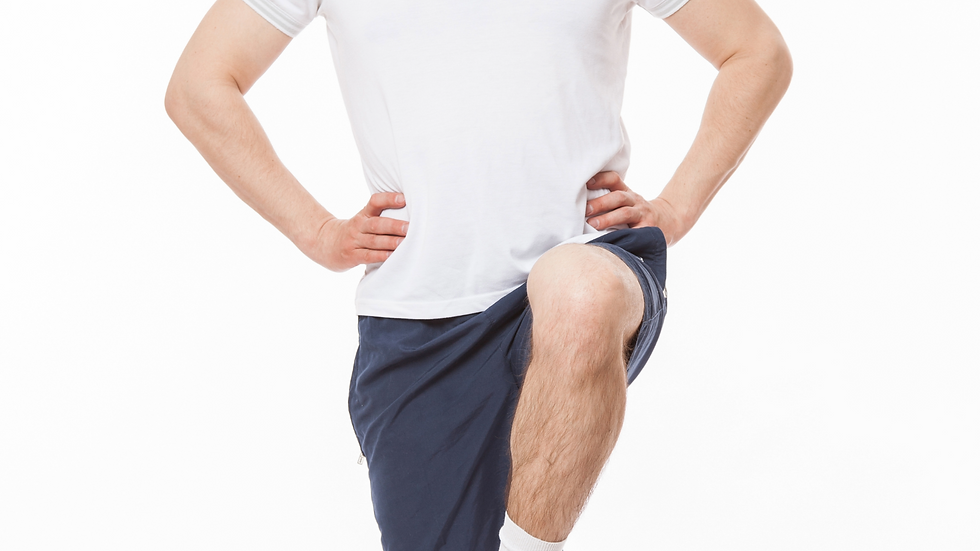
Benefits of the Single-Leg Stance Test
1. Assessing Balance and Stability
The primary advantage of the Single-Leg Stance Test is its effectiveness in assessing balance and stability. For example, athletes in sports like soccer or basketball rely heavily on balance. An improved score in this test can correlate with better performance on the field or court.
2. Identifying Imbalances
By comparing the results from both legs, you can identify imbalances. For instance, if you can only balance for 5 seconds on one leg but 20 seconds on the other, this discrepancy highlights an area that might need focused training.
3. Monitoring Progress
You can administer the Single-Leg Stance Test periodically. Tracking improvements over time can motivate you, especially during recovery from an injury or while striving to reach fitness goals.
4. Enhancing Functional Movement
Exercises based on insights from this test can enhance daily functional movements. Improved balance translates to better performance in routine activities like walking or climbing stairs.
Interpreting Your Results
1. Time Duration
The duration for which you can maintain your balance is a critical indicator of stability. Generally, a time of 10 seconds or more is considered acceptable for most individuals.
2. Comparing Legs
If you find a significant difference—say, 10 seconds versus 18 seconds—this could hint at potential problem areas. Consulting a healthcare professional may help you devise an effective training strategy.
3. Age and Fitness Level Considerations
It's vital to consider that age and fitness level can affect outcomes. Younger individuals often showcase better balance skills than older adults or those less active, highlighting the importance of regular balance training at all ages.
Exercises to Improve Balance
If your results suggest a need for improvement, consider integrating these exercises into your fitness plan:
1. Single-Leg Deadlifts
This exercise targets the hamstrings and glutes while enhancing balance. Stand on one leg, hinge at your hips to lower your torso, and extend the opposite leg behind you. Return to standing and repeat 10-15 times for each leg.
2. Balance Board Training
Using a balance board is an excellent way to boost stability and proprioception. Stand on the board and shift your weight from side to side for about 2-5 minutes daily to improve your balance significantly.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Using Support
Refrain from holding on to walls or furniture during the test. This support may artificially inflate your balance capabilities.
2. Poor Posture
Maintaining proper posture is crucial. Keep your shoulders back and your core engaged during the test to enhance your stability.
Final Thoughts
The Single-Leg Stance Test is a beneficial method for assessing balance and stability. By learning how to execute the test and accurately interpret your results, you can gain valuable insights into your physical health and identify areas that need development.
Including balance training in your workout routine not only improves stability but also lowers the risk of injury and elevates your performance across various activities. Keep an eye on your progress and consult a professional if you identify significant imbalances.

By taking the time to assess and enhance your balance, you are making a positive investment in your long-term health and well-being. So, why not try the Single-Leg Stance Test today?

Services by Dr. Moran Sciamama-Saghiv:




Comments